Astro Authentication: The Complete 2025 Tutorial
Learn how to implement secure authentication in Astro with this comprehensive guide covering SSR setup, protected routes, social login, and production deployment.

Astro is exploding in popularity—over 4 million npm downloads per month and counting. It's fast, flexible, and perfect for everything from content sites to full-stack applications. But if you've tried to find good authentication content for Astro, you've probably noticed: there's almost nothing out there.
Auth0, Clerk, and the other big players have ignored Astro entirely. Their framework guides cover Next.js, Vue, and Svelte, but Astro? Crickets.
This comprehensive Astro authentication tutorial fills that gap. By the end, you'll have production-ready authentication with server-side rendering, protected routes, social login, and deployment best practices—all optimized for Astro's unique architecture.
Why Astro Needs Authentication
First, a quick reality check: when do Astro sites actually need authentication?
Astro's sweet spot is content-heavy sites that benefit from its island architecture and build-time rendering. But increasingly, developers are using Astro for applications that require secure access control:
- SaaS dashboards behind login screens for customer portals
- Member-only content areas on content sites with premium subscriptions
- E-commerce admin panels built with Astro's flexibility and speed
- Internal tools that need role-based access control
- Client portals for agencies and professional services
If you're building any of these, you need authentication. And despite the lack of existing content, Astro authentication works great when you understand its architecture.
Understanding Astro's Architecture for Auth
Before diving into code, let's understand how Astro's architecture affects authentication strategy.
The island architecture means most of your site is static HTML, with interactive "islands" of JavaScript where needed. For authentication, this creates a specific pattern:
- Authentication state lives server-side in cookies or session storage
- Protected pages are rendered server-side with authentication checks
- Interactive islands can access authentication state when they need it
- Static content remains static, keeping performance optimal
Server-side rendering modes matter significantly for authentication:
| Mode | Output Type | Best For Authentication? |
|---|---|---|
output: 'server' | On-demand SSR | ✅ Perfect - pages render per request |
output: 'hybrid' | Mixed static/dynamic | ⚠️ Good - mark auth pages as dynamic |
output: 'static' | Pre-rendered at build | ❌ Not suitable - no runtime auth checks |
For this tutorial, we'll use SSR mode (output: 'server') since it's the most flexible for authentication.
Cookies vs. tokens: In Astro's server-side context, HTTP-only cookies are the natural choice. They're sent automatically with every request, work seamlessly server-side and client-side, and integrate smoothly with Astro's middleware pattern.
Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have:
- ✅ An Astro 4.x project (we'll create one if needed)
- ✅ Node.js 18 or higher installed
- ✅ A AuthHero account (free tier works perfectly)
- ✅ Basic familiarity with Astro's routing and components
Project Setup
Let's start from scratch so everyone's on the same page.
Create a new Astro project:
npm create astro@latest astro-auth-demo
cd astro-auth-demoWhen prompted:
- Choose "Empty" for the template
- Select "Yes" for TypeScript
- Choose "Strict" for TypeScript mode
- Install dependencies when asked
Update Astro config for SSR:
// astro.config.mjs
import { defineConfig } from 'astro/config';
import node from '@astrojs/node';
export default defineConfig({
output: 'server', // Enable server-side rendering
adapter: node({ mode: 'standalone' })
});Install authentication dependencies:
npm install @productname/astroSet up environment variables:
Create a .env file in your project root:
PRODUCTNAME_CLIENT_ID=your_client_id
PRODUCTNAME_CLIENT_SECRET=your_client_secret
PRODUCTNAME_REDIRECT_URI=http://localhost:4321/auth/callbackYou'll get these values from your AuthHero dashboard when you create an application.
Astro-Specific Features Comparison
Understanding Astro's unique features helps you implement authentication effectively:
| Feature | Astro Approach | Authentication Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Islands Architecture | Partial hydration | Auth state available in islands via props |
| File-based Routing | Convention-based | Easy to organize auth routes (/api/auth/*) |
| Middleware System | Request interceptors | Perfect for session validation on every request |
| Multi-framework Support | React, Vue, Svelte, etc. | Auth works with any framework in islands |
| Edge Ready | Deploy to edge platforms | Session validation at the edge for speed |
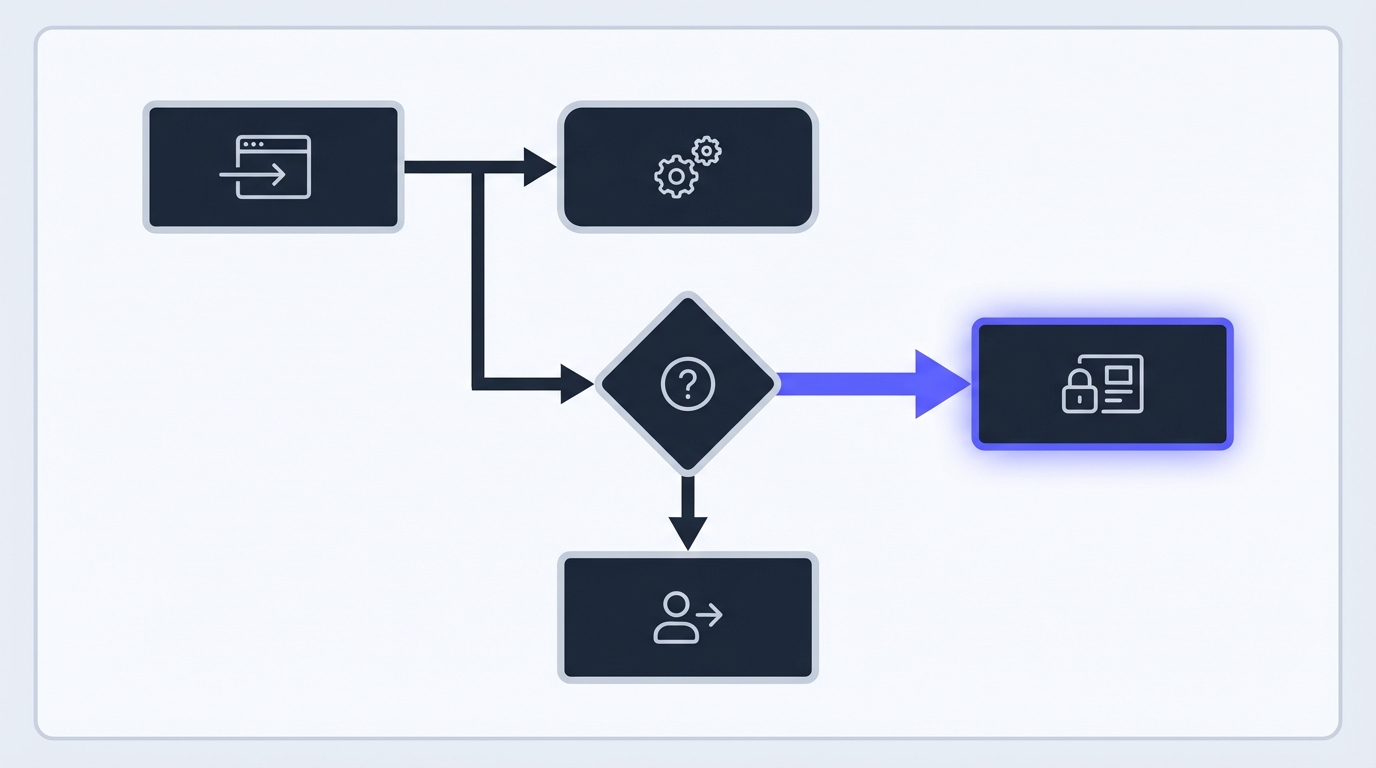
Implementing Authentication
Part A: Server-Side Auth
First, we'll set up the authentication middleware that protects your routes.
Create auth middleware:
// src/middleware/auth.ts
import { defineMiddleware } from 'astro:middleware';
import { getSession } from '@productname/astro';
export const auth = defineMiddleware(async (context, next) => {
// Extract session from cookies
const session = await getSession(context.request);
// Add session to locals so it's available everywhere
context.locals.session = session;
context.locals.user = session?.user || null;
return next();
});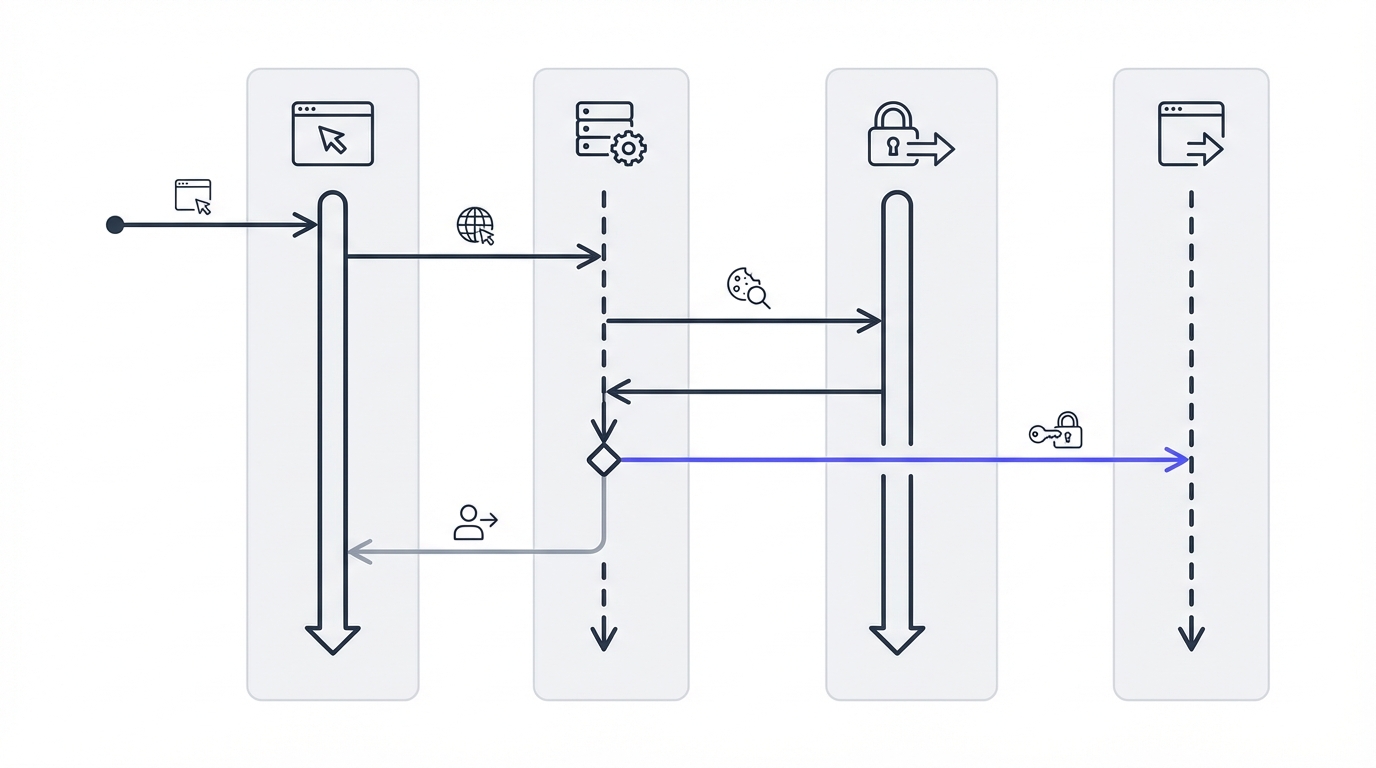
Wire up the middleware:
// src/middleware/index.ts
import { sequence } from 'astro:middleware';
import { auth } from './auth';
// Chain middleware in sequence (add more as needed)
export const onRequest = sequence(auth);Create login and signup pages:
---
// src/pages/login.astro
import Layout from '../layouts/Layout.astro';
const error = Astro.url.searchParams.get('error');
const redirect = Astro.url.searchParams.get('redirect') || '/dashboard';
---
<Layout title="Sign In">
<main class="container">
<h1>Sign In</h1>
{error && (
<div class="error" role="alert">
{error}
</div>
)}
<form action="/api/auth/login" method="POST">
<input type="hidden" name="redirect" value={redirect} />
<div>
<label for="email">Email</label>
<input
type="email"
id="email"
name="email"
autocomplete="email"
required
/>
</div>
<div>
<label for="password">Password</label>
<input
type="password"
id="password"
name="password"
autocomplete="current-password"
required
/>
</div>
<button type="submit">Sign In</button>
</form>
<p>
Don't have an account?
<a href="/signup">Sign up</a>
</p>
</main>
</Layout>Handle auth callbacks:
// src/pages/api/auth/login.ts
import type { APIRoute } from 'astro';
import { login } from '@productname/astro';
export const POST: APIRoute = async ({ request, redirect, cookies }) => {
try {
const formData = await request.formData();
const email = formData.get('email') as string;
const password = formData.get('password') as string;
const redirectTo = formData.get('redirect') as string || '/dashboard';
// Validate inputs
if (!email || !password) {
return redirect('/login?error=Email and password are required', 302);
}
// Authenticate with AuthHero
const { sessionToken } = await login({
email,
password
});
// Set secure session cookie
cookies.set('session', sessionToken, {
httpOnly: true,
secure: import.meta.env.PROD,
sameSite: 'lax',
path: '/',
maxAge: 60 * 60 * 24 * 7 // 7 days
});
return redirect(redirectTo, 302);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Login error:', error);
return redirect('/login?error=Invalid credentials', 302);
}
};// src/pages/auth/callback.ts
import type { APIRoute } from 'astro';
import { handleCallback } from '@productname/astro';
export const GET: APIRoute = async ({ request, redirect, cookies }) => {
try {
const { sessionToken } = await handleCallback(request);
// Set session cookie
cookies.set('session', sessionToken, {
httpOnly: true,
secure: import.meta.env.PROD,
sameSite: 'lax',
path: '/',
maxAge: 60 * 60 * 24 * 7
});
return redirect('/dashboard', 302);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Callback error:', error);
return redirect('/login?error=Authentication failed', 302);
}
};Security Note: Always use
httpOnly: truefor session cookies to prevent XSS attacks. Thesecureflag ensures cookies are only sent over HTTPS in production.
Part B: Protecting Routes
Now let's create protected routes that require authentication.
Create a protected dashboard:
---
// src/pages/dashboard.astro
import Layout from '../layouts/Layout.astro';
const user = Astro.locals.user;
// Redirect unauthenticated users to login
if (!user) {
const redirectUrl = encodeURIComponent(Astro.url.pathname);
return Astro.redirect(`/login?redirect=${redirectUrl}`);
}
---
<Layout title="Dashboard">
<main class="container">
<h1>Welcome, {user.name || user.email}!</h1>
<div class="dashboard-content">
<p>This is your protected dashboard.</p>
<dl class="user-details">
<dt>User ID:</dt>
<dd>{user.id}</dd>
<dt>Email:</dt>
<dd>{user.email}</dd>
</dl>
</div>
<form action="/api/auth/logout" method="POST">
<button type="submit">Sign Out</button>
</form>
</main>
</Layout>Create a reusable protected route helper:
// src/lib/requireAuth.ts
import type { AstroGlobal } from 'astro';
/**
* Require authentication for a page
* Redirects to login if user is not authenticated
* @returns Authenticated user object
*/
export function requireAuth(Astro: AstroGlobal) {
if (!Astro.locals.user) {
const redirectUrl = encodeURIComponent(Astro.url.pathname);
return Astro.redirect(`/login?redirect=${redirectUrl}`);
}
return Astro.locals.user;
}Use it in protected pages:
---
// src/pages/settings.astro
import Layout from '../layouts/Layout.astro';
import { requireAuth } from '../lib/requireAuth';
const user = requireAuth(Astro);
---
<Layout title="Settings">
<main>
<h1>Settings</h1>
<p>Manage your account, {user.name || user.email}</p>
</main>
</Layout>Part C: Client-Side Integration
For interactive islands, you'll want to access authentication state in your React/Vue/Svelte components.
React island example:
// src/components/UserMenu.tsx
import { useEffect, useState } from 'react';
interface User {
id: string;
email: string;
name?: string;
}
export default function UserMenu() {
const [user, setUser] = useState<User | null>(null);
useEffect(() => {
// User data is passed from the server via script tag
const userElement = document.getElementById('user-data');
if (userElement?.textContent) {
try {
const userData = JSON.parse(userElement.textContent);
setUser(userData);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to parse user data:', error);
}
}
}, []);
if (!user) {
return (
<a href="/login" className="btn">
Sign In
</a>
);
}
return (
<div className="user-menu">
<span>Hello, {user.name || user.email}</span>
<form action="/api/auth/logout" method="POST">
<button type="submit">Sign Out</button>
</form>
</div>
);
}Pass user data from Astro to islands:
---
// src/layouts/Layout.astro
import UserMenu from '../components/UserMenu';
const user = Astro.locals.user;
---
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>{title}</title>
</head>
<body>
{user && (
<script
id="user-data"
type="application/json"
set:html={JSON.stringify(user)}
/>
)}
<nav>
<UserMenu client:load />
</nav>
<slot />
</body>
</html>Building Common Auth Features
Now let's add essential authentication features that every application needs.
Logout functionality:
// src/pages/api/auth/logout.ts
import type { APIRoute } from 'astro';
export const POST: APIRoute = async ({ cookies, redirect }) => {
// Clear session cookie
cookies.delete('session', { path: '/' });
return redirect('/', 302);
};Password reset flow:
---
// src/pages/reset-password.astro
import Layout from '../layouts/Layout.astro';
const success = Astro.url.searchParams.get('success');
const error = Astro.url.searchParams.get('error');
---
<Layout title="Reset Password">
<main class="container">
<h1>Reset Your Password</h1>
{success && (
<div class="success" role="alert">
Check your email for a password reset link.
</div>
)}
{error && (
<div class="error" role="alert">
{error}
</div>
)}
<form action="/api/auth/reset-password" method="POST">
<div>
<label for="email">Email Address</label>
<input
type="email"
id="email"
name="email"
autocomplete="email"
required
/>
</div>
<button type="submit">Send Reset Link</button>
</form>
<p>
Remember your password?
<a href="/login">Sign in</a>
</p>
</main>
</Layout>Adding Social Logins
Social authentication works seamlessly with Astro's request/response model. Here's how to add Google and GitHub.
---
// src/pages/login.astro (updated)
import Layout from '../layouts/Layout.astro';
const error = Astro.url.searchParams.get('error');
---
<Layout title="Sign In">
<main class="container">
<h1>Sign In</h1>
{error && (
<div class="error" role="alert">{error}</div>
)}
<div class="social-login">
<a href="/api/auth/google" class="btn btn-google">
<svg width="18" height="18" viewBox="0 0 18 18">
<!-- Google icon SVG -->
</svg>
Sign in with Google
</a>
<a href="/api/auth/github" class="btn btn-github">
<svg width="18" height="18" viewBox="0 0 18 18">
<!-- GitHub icon SVG -->
</svg>
Sign in with GitHub
</a>
</div>
<div class="divider">
<span>or continue with email</span>
</div>
<form action="/api/auth/login" method="POST">
<!-- Email/password form fields -->
</form>
</main>
</Layout>// src/pages/api/auth/google.ts
import type { APIRoute } from 'astro';
import { getAuthorizationUrl } from '@productname/astro';
export const GET: APIRoute = async ({ redirect }) => {
const authUrl = await getAuthorizationUrl({
provider: 'google',
redirectUri: import.meta.env.PRODUCTNAME_REDIRECT_URI,
// Request specific scopes
scope: ['email', 'profile']
});
return redirect(authUrl, 302);
};// src/pages/api/auth/github.ts
import type { APIRoute } from 'astro';
import { getAuthorizationUrl } from '@productname/astro';
export const GET: APIRoute = async ({ redirect }) => {
const authUrl = await getAuthorizationUrl({
provider: 'github',
redirectUri: import.meta.env.PRODUCTNAME_REDIRECT_URI,
scope: ['user:email']
});
return redirect(authUrl, 302);
};Astro Integration Checklist
Use this checklist to ensure your authentication implementation is complete:
- [ ] SSR Mode Enabled:
output: 'server'inastro.config.mjs - [ ] Middleware Configured: Auth middleware in
src/middleware/ - [ ] Session Validation: Session checked on every request
- [ ] Protected Routes: Helper function for route protection
- [ ] Login/Signup Pages: Both email and social options
- [ ] Logout Functionality: Cookie cleared properly
- [ ] Error Handling: User-friendly error messages
- [ ] Redirect Preservation: Return to original page after login
- [ ] Island Integration: User data passed to interactive islands
- [ ] Environment Variables: API keys never committed to git
Production Considerations
Before deploying your Astro authentication to production, implement these critical security measures.
Security headers middleware:
// src/middleware/security.ts
import { defineMiddleware } from 'astro:middleware';
export const security = defineMiddleware(async (context, next) => {
const response = await next();
// Set security headers
response.headers.set(
'Strict-Transport-Security',
'max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload'
);
response.headers.set('X-Frame-Options', 'DENY');
response.headers.set('X-Content-Type-Options', 'nosniff');
response.headers.set('X-XSS-Protection', '1; mode=block');
response.headers.set(
'Content-Security-Policy',
"default-src 'self'; script-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline'"
);
return response;
});Session configuration best practices:
Use secure, HTTP-only cookies in production with appropriate expiry:
// Production cookie configuration
const sessionCookie = {
httpOnly: true, // Prevent XSS attacks
secure: true, // HTTPS only
sameSite: 'lax', // CSRF protection
path: '/', // Available site-wide
maxAge: 60 * 60 * 24 * 7 // 7 days
};Deployment platform configuration:
Astro with SSR works on all major platforms. Here's the adapter configuration for each:
| Platform | Adapter | Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Vercel | @astrojs/vercel | Auto-detected, zero config |
| Netlify | @astrojs/netlify | Set publish directory to dist |
| Cloudflare Pages | @astrojs/cloudflare | Edge-optimized SSR |
| Node.js | @astrojs/node | Standalone or middleware mode |
| Deno | @astrojs/deno | Deploy to Deno Deploy |
Vercel deployment example:
// astro.config.mjs
import { defineConfig } from 'astro/config';
import vercel from '@astrojs/vercel/serverless';
export default defineConfig({
output: 'server',
adapter: vercel({
webAnalytics: { enabled: true }
})
});Netlify deployment example:
// astro.config.mjs
import { defineConfig } from 'astro/config';
import netlify from '@astrojs/netlify/functions';
export default defineConfig({
output: 'server',
adapter: netlify()
});Cloudflare Pages deployment:
// astro.config.mjs
import { defineConfig } from 'astro/config';
import cloudflare from '@astrojs/cloudflare';
export default defineConfig({
output: 'server',
adapter: cloudflare({
mode: 'directory' // or 'advanced'
})
});Troubleshooting Common Issues
Cookies not working in development
Problem: Session cookies aren't being set or read correctly.
Solution: Make sure you're accessing your local server via http://localhost:4321, not 127.0.0.1. Some browsers handle cookies differently for IP addresses versus hostnames.
# ✅ Correct
http://localhost:4321
# ❌ May cause cookie issues
http://127.0.0.1:4321OAuth redirect mismatches
Problem: OAuth flows fail with redirect URI mismatch errors.
Solution: Double-check that your redirect URI in the AuthHero dashboard exactly matches what you're using in code. Include the protocol (http:// or https://) and ensure there are no trailing slashes unless your callback expects them.
// In AuthHero dashboard: http://localhost:4321/auth/callback
// In code:
PRODUCTNAME_REDIRECT_URI=http://localhost:4321/auth/callbackHydration errors with auth state
Problem: React/Vue/Svelte islands show hydration mismatches when displaying user data.
Solution: Use client:load instead of client:idle to ensure the component hydrates immediately. Also, ensure server-rendered HTML matches what the client expects.
<!-- ✅ Correct -->
<UserMenu client:load />
<!-- ❌ May cause hydration issues -->
<UserMenu client:idle />Session not persisting across requests
Problem: Users get logged out between page navigations.
Solution: Verify your cookie configuration includes the correct path, sameSite, and maxAge values:
cookies.set('session', token, {
path: '/', // Available site-wide
sameSite: 'lax', // Required for navigation
maxAge: 60 * 60 * 24 * 7 // Explicit expiry
});Middleware not running
Problem: Session validation doesn't happen on some routes.
Solution: Ensure you've exported onRequest from src/middleware/index.ts and that the middleware directory exists at the project root:
// src/middleware/index.ts
export { onRequest } from './auth';Quick Troubleshooting Table
| Issue | Common Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Cookies not set | Using IP address instead of localhost | Use http://localhost:4321 |
| OAuth redirect fails | URI mismatch in provider config | Match URIs exactly including protocol |
| Hydration errors | Wrong client directive | Use client:load for auth components |
| Session expires immediately | Missing maxAge in cookie | Set explicit maxAge value |
| Middleware not running | Missing export | Export onRequest from middleware |
Next Steps
You now have a fully functional authentication system in Astro that follows best practices and works seamlessly with the framework's architecture. From here, you can extend it with:
- Multi-factor authentication for security-conscious users [Link: /docs/mfa]
- Organization/team support for B2B applications [Link: /docs/organizations]
- Role-based access control for different user types [Link: /docs/rbac]
- User profile management with custom fields [Link: /docs/profiles]
- Email verification flows for enhanced security [Link: /docs/email-verification]
The beauty of starting with a solid foundation is that these advanced features become straightforward additions rather than architectural challenges.
Astro Authentication Architecture Diagram
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Client Request │
└──────────────────┬──────────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Astro Middleware Layer │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ 1. Extract session cookie │ │
│ │ 2. Validate with AuthHero │ │
│ │ 3. Attach user to context.locals │ │
│ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
└──────────────────┬──────────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Astro Page/Route │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Access user via Astro.locals.user │ │
│ │ Render protected content or redirect │ │
│ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
└──────────────────┬──────────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Interactive Islands (Optional) │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Receive user data via props or script tag │ │
│ │ React/Vue/Svelte components with auth state │ │
│ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘Ready to add authentication to your Astro app? AuthHero provides a complete Astro SDK with server-side session management, social logins, and everything you need to ship authentication in an afternoon. Get your API keys in 30 seconds →